Otitis media
Otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear. The term includes several
different disease entities. A good understanding of terms is essential.
Acute otitis media
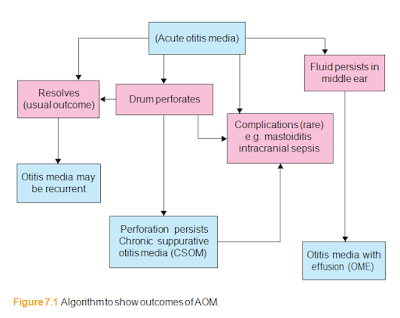
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a short-lived (usually 1–5 days) infection of the middle ear. If it is viral it may last as little as a day or so but it can persist, causing pus to accumulate under pressure behind the eardrum, which may perforate (Fig. 7.1). Before the eardrum perforates, AOM is intensely painful. It mainly occurs in children.
Recurrent otitis media (ROM) refers to repeated such episodes, typically more than three in a 6-month period.
Otitis media with effusion
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is also common in children. Fluid – often thick sticky ‘glue’ – accumulates in the middle ear behind an intact drum. Because some fluid in the middle ear is normal for up to several weeks after an episode of AOM, the term OME requires that the fluid be persistent for at least 3 months.
Chronic otitis media
This implies that the eardrum has perforated, the perforation has failed to heal and there is ongoing infection. The term chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is of- ten used to emphasize the tendency for ears with longstanding perforations to be- come infected and discharge.
Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is the accumulation of squamous epithelium in the middle ear, usu- ally in an ear with a longstanding perforation. This is the most serious form of CSOM.


ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق
من فضلك اكتب تعليقا مناسبا